When considering online privacy, the notion of a DNS leak might not be the first aspect that comes to mind. However, it’s crucial to understand it, as it’s a potential risk to one’s online security. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what is a DNS leak, how to diagnose it, and propose a set of solutions for DNS leak protection.
Breaking Down the Concept of DNS Leak
What is DNS?
The Domain Name System, often referred to as DNS, is a fundamental component of the internet that allows us to navigate the vast digital world smoothly. It functions somewhat like a phone book for the internet, translating human-friendly website names into computer-friendly IP addresses. It’s an essential part of how we access information online, yet most users aren’t aware of its existence or its vital role.
Domain Names
Every website you visit has a unique identifier known as a domain name. These are the website names that we type into our browsers, such as google.com or wikipedia.org. Domain names were created to make it easier for humans to remember and access websites, as it would be incredibly challenging to remember the string of numbers that make up an IP address.
IP Addresses
An IP address is a unique string of numbers and/or letters that identifies a device on the internet. Every device that is connected to the internet has an IP address, and all the data sent over the internet is directed towards these addresses. However, these addresses are often long and complicated, which is why we use domain names instead.
DNS Servers
DNS servers are the machines that handle the task of translating domain names into IP addresses. When you type a domain name into your browser, your request first goes to a DNS server. This server then looks up the corresponding IP address and sends the information back to your device. Without DNS servers, the process of finding the right IP address for a given domain name would be much slower and more complicated.
The Resolution Process
When you type in a URL (like www.google.com) into your browser, a process called DNS resolution occurs. Here’s a simplified version of what happens:
- Your browser asks your computer if it already knows the IP address for the requested domain name. If it does, the process ends here, and the website loads.
- If your computer doesn’t know the IP address, it sends a query to a DNS resolver. The resolver is usually configured by your internet service provider (ISP).
- If the resolver doesn’t know the IP address, it sends the query to one of the root DNS servers. These servers know where to find information about top-level domains (like .com, .org, etc.).
- The root server will then direct the resolver to a TLD (Top-Level Domain) server, which holds information about the specific domain.
- The TLD server then directs the resolver to the server that hosts the domain’s information. This server provides the IP address for the domain.
- The resolver then gives this IP address to your browser, which can finally load the website.
Importance of DNS
By translating domain names into IP addresses, DNS makes the internet far more user-friendly. Without DNS, we would need to remember complex IP addresses for each website we want to visit. By acting as the phone book for the internet, DNS saves us time and makes the process of accessing websites significantly more straightforward and efficient.
Moreover, DNS also plays a crucial role in email services, online gaming, and virtually all other online activities. It helps route traffic efficiently, prevent phishing attacks, and even manage and control spam emails. Therefore, DNS is not just a convenience but a necessity for the smooth functioning of the internet.
In conclusion, the DNS is an essential, albeit invisible, cornerstone of the internet. It operates quietly in the background, making our digital lives easier and more efficient. Understanding how it works can provide us with a greater appreciation for the complexity and brilliance that underpins our digital world.
DNS Leak: A Detailed Overview

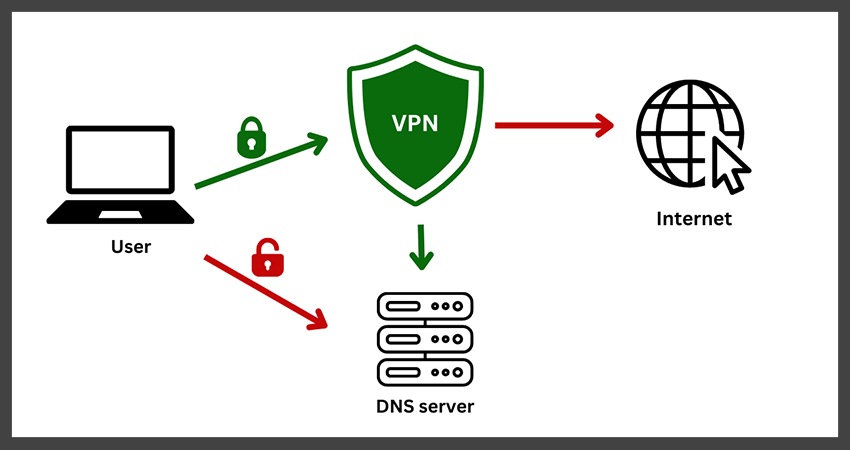
DNS leaks represent a significant security flaw in the realm of internet browsing and data privacy. They occur when DNS requests—essentially queries made by your device to translate a domain name to an IP address—are sent to your Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) DNS servers, despite using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for protection.
This undesirable situation may arise due to a variety of reasons. An improperly configured VPN, ineffective VPN service, lack of IPv6 support, usage of transparent DNS proxies by ISPs, and Windows features like the smart multi-homed name resolution and Teredo, can all lead to DNS leaks.
The risks associated with DNS leaks are significant. In essence, they can expose a user’s online activities and IP address to their ISP, third-party organizations, and potential threat actors. This can lead to privacy compromises, slowed internet connections, and potentially, the risk of accessing malicious websites.
Prevention of DNS leaks primarily involves the correct configuration of your VPN service, ensuring that it connects only to its own DNS servers. Using a reputable VPN service with robust DNS leak protection features is also crucial. Regular testing for DNS leaks using reliable online tools can help detect and rectify any leaks, ensuring your online privacy and security.
Unmasking the Causes of a DNS Leak

Misconfigured VPN
In some instances, a DNS leak could be attributed to an improperly set up VPN. This situation may arise when a VPN erroneously assigns a DNS server that belongs to the user’s ISP instead of one from its own network.
VPN Without Its Own DNS Servers
Some VPN services lack proprietary DNS servers, making them susceptible to DNS leaks. If a VPN service relies on third-party DNS servers, it could inadvertently cause a user’s DNS requests to leak outside the VPN’s encrypted tunnel.
Non-Support of IPv6
The internet era witnessed an evolution from the 32-bit IPv4 addresses to the more advanced 128-bit IPv6 addresses. However, not all VPNs support this newer technology. This discrepancy can result in DNS requests spilling out of the encrypted VPN tunnel.
Transparent DNS Proxies
Certain ISPs have started forcing customers to use their DNS servers, even when users opt for third-party VPN settings. This action results in a transparent proxy that redirects the user’s online activities back to their ISP’s DNS servers, causing a DNS leak.
Issues with Windows Smart Features
Microsoft, in its Windows 8 and onwards operating systems, introduced a feature called Smart Multi-Homed Name Resolution (SMHNR). This feature sends DNS requests to all available servers and accepts the first response. However, this could lead to a DNS leak and expose users to spoofing attacks.
Windows Teredo Issues
To facilitate the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, Windows has a built-in feature called Teredo. While it helps both IP systems coexist, it poses a significant security risk for VPN users. Teredo can override a user’s encrypted VPN tunnel, resulting in a DNS leak.
The Seriousness of a DNS Leak

A DNS leak can have serious implications. It compromises the very reasons for which a user deploys a VPN service. If a DNS leak occurs, the user’s private information, including browsing activity, IP address, and location, can be exposed to their ISP, third-party organizations, and malevolent actors monitoring network activity.
Identifying a DNS Leak
There are tools available for users to check if their DNS is leaking. Many VPN suppliers and vendors provide such tests. These tests provide information about the DNS server to which the user is connected and offer further insights about their browsing session.
How Does a DNS Leak Test Work?
A DNS leak test provides users with information about their VPN connection, including the active IP address and location. This information can be contrasted against their real IP address and location, providing a practical way to check for a DNS leak.
Safety of DNS Leak Tests
Reputable VPN providers offer DNS leak tests that are safe and secure. However, users should be wary of tests from untrusted providers.
Fixing a DNS Leak
A standard DNS leak can be mitigated by configuring a VPN to connect only to its own DNS servers. This forces a computer to use only the VPN’s DNS servers, preventing connection to the user’s ISP.
Preventing a DNS Leak
Understanding what a DNS leak is, is the first step towards preventing it. A well-configured VPN server is an effective way to ensure anonymous browsing, thereby preventing a DNS leak.
Set Up Your Own VPN in a Different Country
One can reduce the probability of DNS leaks by setting up a private VPN in a different country where ISPs are less likely to leak information. While this is not a foolproof way, it can reduce the occurrence of leaks.
Use an Anonymous Web Browser
Using an anonymous web browser, like Tor, can prevent DNS leaks. Such browsers don’t require DNS configuration at the operating system level, offering total anonymity during browsing sessions.
Use a Firewall
Implementing a firewall can help prevent DNS leaks. A firewall can block data, including DNS requests, from leaving your computer, thereby ensuring your online activities remain private.
Set-up a Nonexistent DNS
Another way to prevent DNS leaks is by configuring your DNS server to a nonexistent one. This can be achieved via a UNIX/Linux terminal or a GUI.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what is a DNS leak, its potential risks, and ways to prevent it can help ensure your online privacy. Remember, it’s not just about browsing anonymously, but also about maintaining your online security.
Please note that this article is intended to provide a comprehensive understanding of a DNS leak and its potential solutions. Always consult with a qualified professional if you encounter any issues with your VPN or DNS settings.
“Remember, it’s not just about browsing anonymously, but also about maintaining your online security.”
For more information on how to fix a DNS leak, prevent DNS leak, how to test for DNS leak, or for VPN with DNS leak protection, visit anonymistic.com.





