In our technologically advancing world, devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and desktop computers have become indispensable. These gadgets rely on various connectivity technologies like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and Cellular networks to communicate with each other and the internet. This article delves into these technologies, elucidating their workings, differences, and importance in our daily lives.
Wi-Fi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide high-speed internet and network connections.
Ethernet, on the other hand, is a wired connection that links devices within a local area network (LAN), such as computers within a home or office.
Cellular networks, as the name suggests, are wireless networks that use mobile phone signals to connect to the internet.
Each of these technologies has its unique advantages and use cases, which we will explore in the following sections.
The Internet: A Global Communication Network
The internet, in its vast and expansive nature, is a global network that connects millions upon millions of computer systems across every corner of the world.
It’s a technological marvel that can be best visualized as a communication language specifically designed for computers. This communication is facilitated by a universally accepted protocol known as TCP/IP, which serves as a common language among a diverse range of devices.

When you, as a user, access a particular website, what essentially happens is that your computer sends a specific request to the server where the website is hosted.
This server, acting as a middleman, then delivers the requested information back to your computer. This process enables you to view the webpage on your screen. However, it’s crucial to understand that the server is not synonymous with the internet.
The internet, in its true essence, comprises the networks created by all the connected computers globally. In other words, the internet is a complex and intricate network of networks. It’s a web of interconnected systems that facilitates global communication and data exchange.
Ethernet: The Local Area Link
Ethernet, which bears a resemblance to the internet in terms of its functionality, is predominantly utilized to establish connections between various devices within the confines of a local area network, also known as a LAN.
This essentially makes it a more compact and localized system of connection, as opposed to the vast and global nature of the internet.

When it comes to accessing the internet, there are primarily two methods that are commonly employed:
- Firstly, one can gain access through an internet service provider, often abbreviated as ISP. This is a company that provides the services and infrastructure necessary for internet connectivity.
- Secondly, one can use a cellular modem or a mobile phone that has a data plan provided by a cellular carrier. This allows for internet access even when one is on the move.
Each and every device that is either directly or indirectly connected to the internet is assigned a unique internet protocol address, more commonly known as an IP address.
These IP addresses play a crucial role in enabling computers and other devices to identify each other during the process of sending and receiving information over the internet. This ensures that the information reaches its intended destination without any mix-ups or errors.
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Wired vs Wireless
Ethernet involves wired communication between devices. Devices connected via Ethernet cables to a central switch or hub can share data, large files, and resources among each other.
The wired connection bypasses obstacles like walls and furniture that could interfere with the signal strength, resulting in faster speeds, lower latency, and better security.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi accomplishes most of this wirelessly. Although more convenient, Wi-Fi is typically slower than Ethernet.
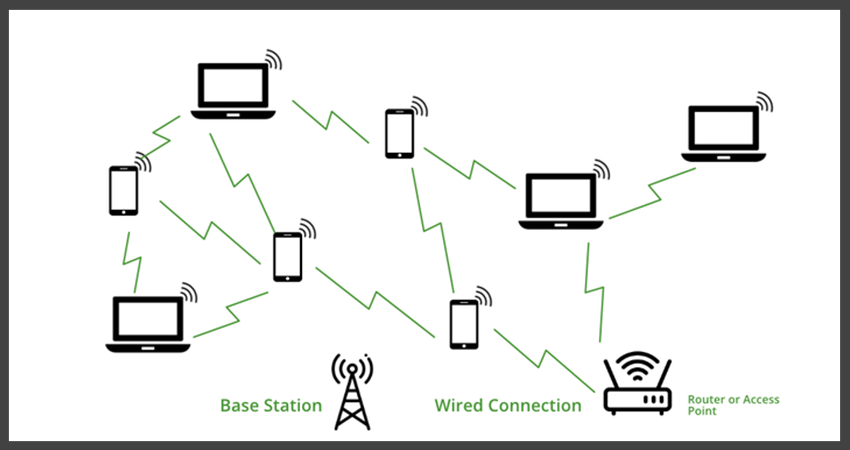
Wi-Fi allows wireless devices to communicate with each other and access the internet without the need for physical connections.
However, Wi-Fi signals can be affected by factors such as distance, physical obstructions, and interference from other devices.
Therefore, while Wi-Fi offers the convenience of mobility, it may not always provide the most stable or secure connection.
For tasks that require high-speed data transfer or a stable connection, such as online gaming or video conferencing, Ethernet is often the preferred choice.
Wi-Fi: A Wireless Home Network
Wi-Fi, which is also known as Wireless Fidelity, is a technology that establishes a wireless home network.
This network allows devices that are connected to it to communicate with each other seamlessly and access the internet without the need for wired Ethernet connections, network cables, or any other types of physical connections.
This eliminates the clutter and inconvenience of wires and cables, making it a popular choice for many households and businesses.
To establish a wireless internet connection via Wi-Fi, certain equipment is necessary. This includes a modem that is connected to a wireless router through Ethernet cables.

Alternatively, a wireless gateway can be used, which is a device that combines the functions of a modem and a router.
These devices connect to an internet service provider, which provides the actual internet access. This setup allows for the wireless transmission of internet signals, enabling devices to connect to the internet without the need for physical connections.
Despite the convenience of wireless connections, there are instances where wired connections, like Ethernet, are more suitable.
Ethernet connections, for instance, are less prone to interference and can provide faster and more stable connections. This makes them ideal for tasks that require high-speed data transfer or a stable connection, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
Bluetooth: A Short-Range Connection
Bluetooth is a type of wireless technology that has been designed specifically to enable different devices to exchange data over relatively short distances.
This technology is commonly used to pair mobile devices, such as smartphones or tablets, with other mobile devices or even with fixed devices, like desktop computers or smart home systems.
Contrary to what many people might believe, Bluetooth operates independently of Wi-Fi and cellular connections.
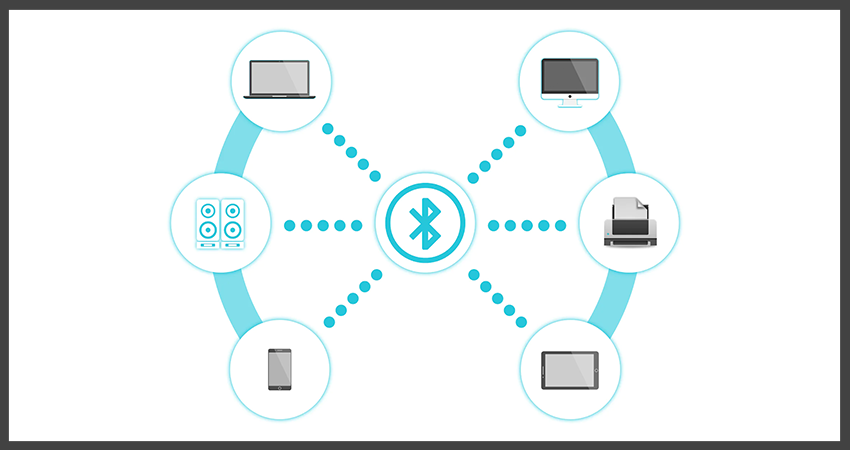
To illustrate, consider a scenario where a keyboard is being paired with a tablet. This pairing can be achieved without the need for an internet signal, demonstrating that Bluetooth can function independently of other types of connections.
However, it’s important to note that while Bluetooth can facilitate basic device pairing and data exchange, some features on mobile devices may still require a Wi-Fi or cellular connection to be accessed.
This means that while Bluetooth is a powerful tool for device connectivity, it’s not a complete replacement for other forms of wireless communication.
Cellular Networks: A Wireless Connection Anywhere

Cellular networks, which are commonly referred to as mobile networks, are designed to provide wireless connections. These connections are made possible through the use of cellular towers that are strategically placed to ensure optimal coverage.
In order to gain access to these networks, one must establish a connection through a cellular service provider. Examples of such providers include, but are not limited to, AT&T, T-Mobile, Verizon, and Sprint.
In addition to providing wireless connections for mobile devices, cellular networks also have the capability to broadcast a Wi-Fi signal. This can be achieved through the use of a portable Wi-Fi hotspot or a cellular modem.
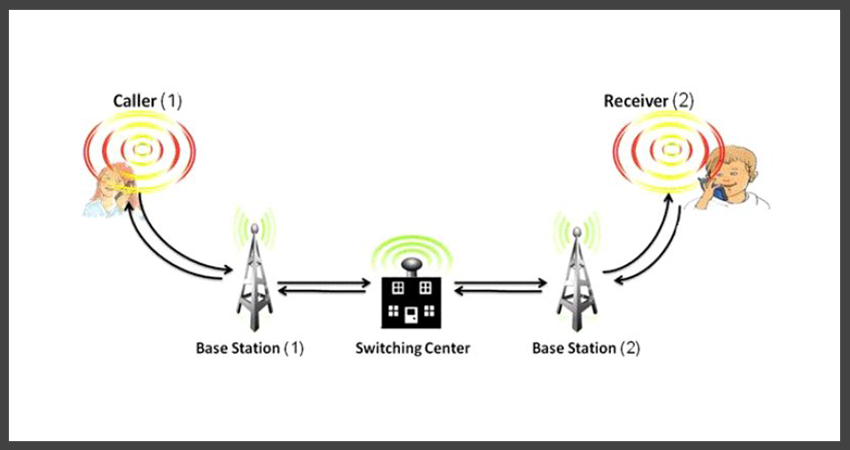
These devices, once connected to the cellular network through a cellular provider, have the ability to convert cellular data into a Wi-Fi signal. This conversion allows for the use of Wi-Fi-enabled devices in areas where a traditional Wi-Fi network may not be available.
However, it’s important to note that while cellular networks can provide internet access in areas without traditional Wi-Fi, they are often subject to data limits and can incur additional charges if these limits are exceeded.
Furthermore, the quality of the connection can vary based on the proximity to a cellular tower and the number of users accessing the network at the same time.
Therefore, while cellular networks offer a level of convenience and mobility, they may not always provide the most reliable or cost-effective solution for internet access.
In Summary: The Differences Between Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and Cellular Networks
Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and Cellular technologies establish wired or wireless communication networks between multiple devices. Their main differences lie in the speeds at which they transmit information, the distance over which the data can be sent, how they interact with other devices, and their operational scale (WAN vs LAN).
Figuring out the best connectivity option for your needs can be complex, but understanding how these technologies work can make the decision easier.
With the right choice, you can enjoy seamless connectivity, whether you’re browsing the web at home, streaming videos on the go, or transferring large files within your local network.





